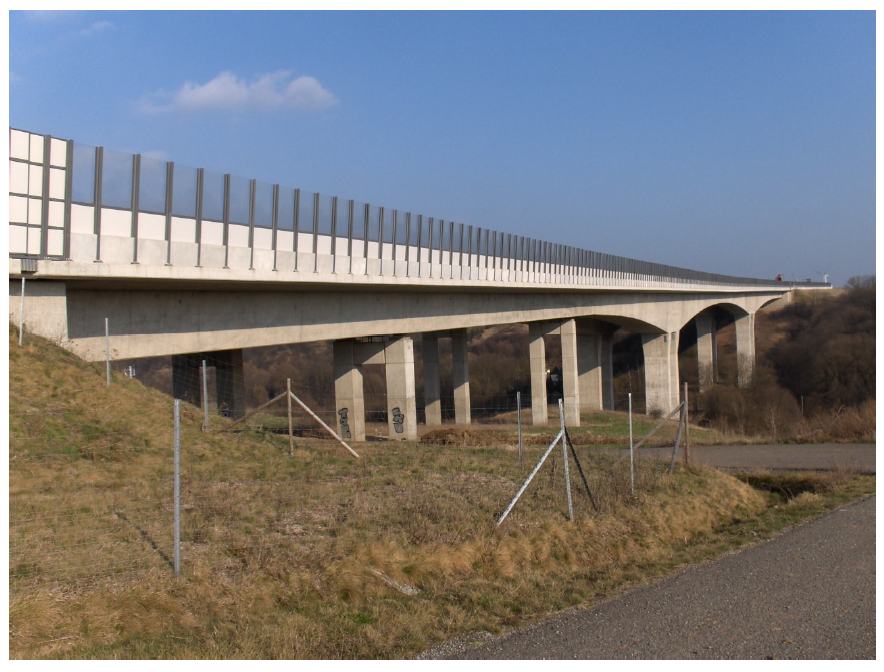
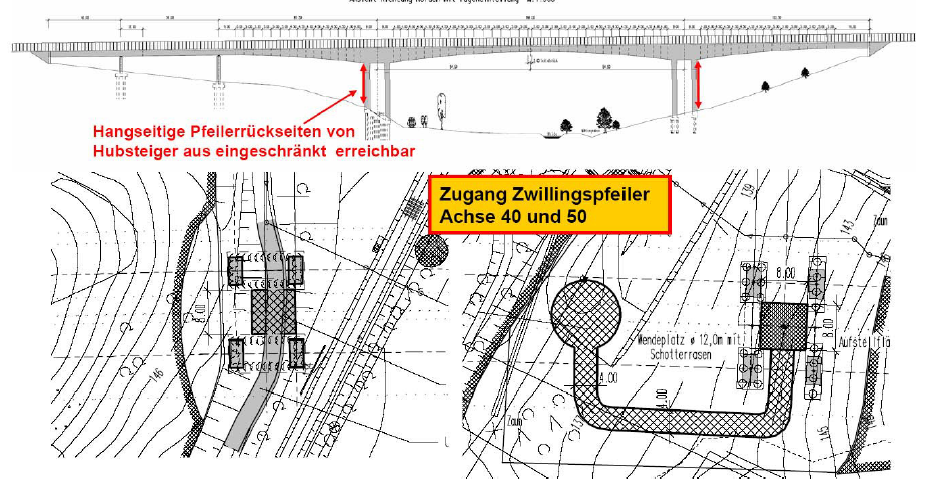
The Weidatalbrücke crosses the Weidatal at a height of approx. 45 m on the A38 federal motorway near Esperstedt. The separate superstructures with prestressed concrete box girder cross-sections have spans of 40.00 / 54.00 / 87.50 / 169.00 and 102.50 m. All pillars are designed as non-accessible reinforced concrete cross-sections. The superstructures are constructed using a mixed construction method and are prestressed with internal tendons in the carriageway and floor slab and external tendons in the box girder. The structure is deeply founded in axes 10 to 50 on large bored piles. The diameter is in axis 10 to 30 and in axis 50 1.30m and in axis 40 1.50m. The abutment axis 60 is flat in the slope. Due to the slope thrust to be taken into account, the foundation of the axis 40 pillar consists of an overlapping bored pile wall arranged in the shape of a box.
Object description
(No object description available.)
Civil engineering type
:
Year of construction
:
2007
Composed of materials
:
Location coordinates
:
51° 24' 57.51" N, 11° 39' 54.67" E
Country
:
Loading map...
{"minzoom":false,"maxzoom":false,"mappingservice":"leaflet","width":"auto","height":"350px","centre":false,"title":"","label":"","icon":"","lines":[],"polygons":[],"circles":[],"rectangles":[],"copycoords":false,"static":false,"zoom":false,"defzoom":6,"layers":["OpenStreetMap"],"image layers":[],"overlays":[],"resizable":false,"fullscreen":false,"scrollwheelzoom":true,"cluster":false,"clustermaxzoom":20,"clusterzoomonclick":true,"clustermaxradius":80,"clusterspiderfy":true,"geojson":"","clicktarget":"","imageLayers":[],"locations":[{"text":"\u003Cdiv class=\"mw-parser-output\"\u003E\u003Cp\u003EWeidatalbr\u00fccke (RFB G\u00f6ttingen)\n\u003C/p\u003E\u003C/div\u003E","title":"Weidatalbr\u00fccke (RFB G\u00f6ttingen)\n","link":"","lat":51.415975,"lon":11.665186111111112,"icon":"/images/imsafe/c/c8/Blue-marker.png"}],"imageoverlays":null}
Object analysis
The testing of external tendons is one of the focal points. With a test matrix, the test methods are compiled in the course of the main test and, in the event of anomalies, also as part of an object-related damage analysis, and a recommendation for the scope of the test is given. The examination includes a visual examination of the anchorages, the tendons and deflections as well as an endoscopic examination of the anchorage area and the deflections. Furthermore, a gradient measurement of the superstructure, a tensioning force determination via frequency measurement, magnetic inductive tendon testing, an ultrasonic test of the tendon anchorages, a tensioning force zero measurement with the frequency method, an inclinometer measurement and a geodetic measurement were carried out. A test matrix summarizes the recommended test methods, the scope of tests and the frequency of tests on the external tendons of the Weidatal Bridge as a supplement to DIN 1076.
Object state
The results of the clamping force measurement indicate that the actual time-dependent deformations from creep and shrinkage are greater than assumed in the static calculation. Apparently the creep and shrinkage processes at the bridge are not yet complete. The measurement results of the inclinometer measurement and the final geodetic measurement from the construction phase were used as reference measurements. As a result, no significant shifts in the slope were found. The movement down the slope is approx. 2 mm over the entire measurement period. This also corresponds to the maximum value that was recorded at the geodetic measuring points and is therefore not critical.
Observed deterioration processes
:
Observed damage types
:
Performance indicators
:
Deformation, Load bearing capacity, Spatial properties (concrete cover/duct voids)
Images
Documents
This case study was contributed by Florian Fliegel of AEC3. Last edited by technical staff.