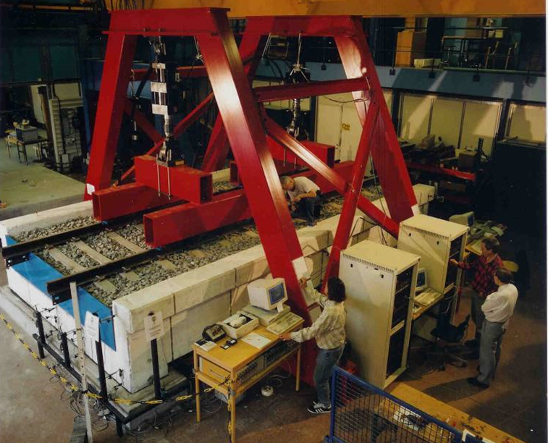
Concrete Trough Bridges on the Iron Ore Railway Line (case study)
An increase of the axle load from 250 kN to 300 kN was planned on the iron ore railway Luleå – Kiruna – Narvik. The fatigue capacity of the exisiting concrete trough bridges was too low according to current codes. A research program was started where the fatigue capacity was investigated, Elfgren et al. (1996). Thun et al. (2000).
Object description
(No object description available.)
Civil engineering type
:
Railway network Bridge
Year of construction
:
1967
Composed of materials
:
Location coordinates
:
66° 34' 13.50" N, 21° 1' 15.63" E
Country
:
Object analysis
In a research program, loads and deflections were monitored on four bridges along the line. One bridge, that had been taken out of service, was transported to Luleå University of Technology. It was there tested in fatigue with the planned axle load.
Case type
:
Research
Object state
In tests, it was found that the bridge could withstand 6 million load cycles at 360 kN without any signs of distress. Only hairline concrete cracks could be seen. It could be concluded that the codes were quite conservative regarding fatigue.
Observed deterioration processes
:
Observed damage types
:
Performance indicators
:
Displacement, Traffic information via WIM/BWIM, Load bearing capacity
Images
Documents
This case study was contributed by Frida Liljefors of Norwegian University Of Science And Technology. Last edited by technical staff.